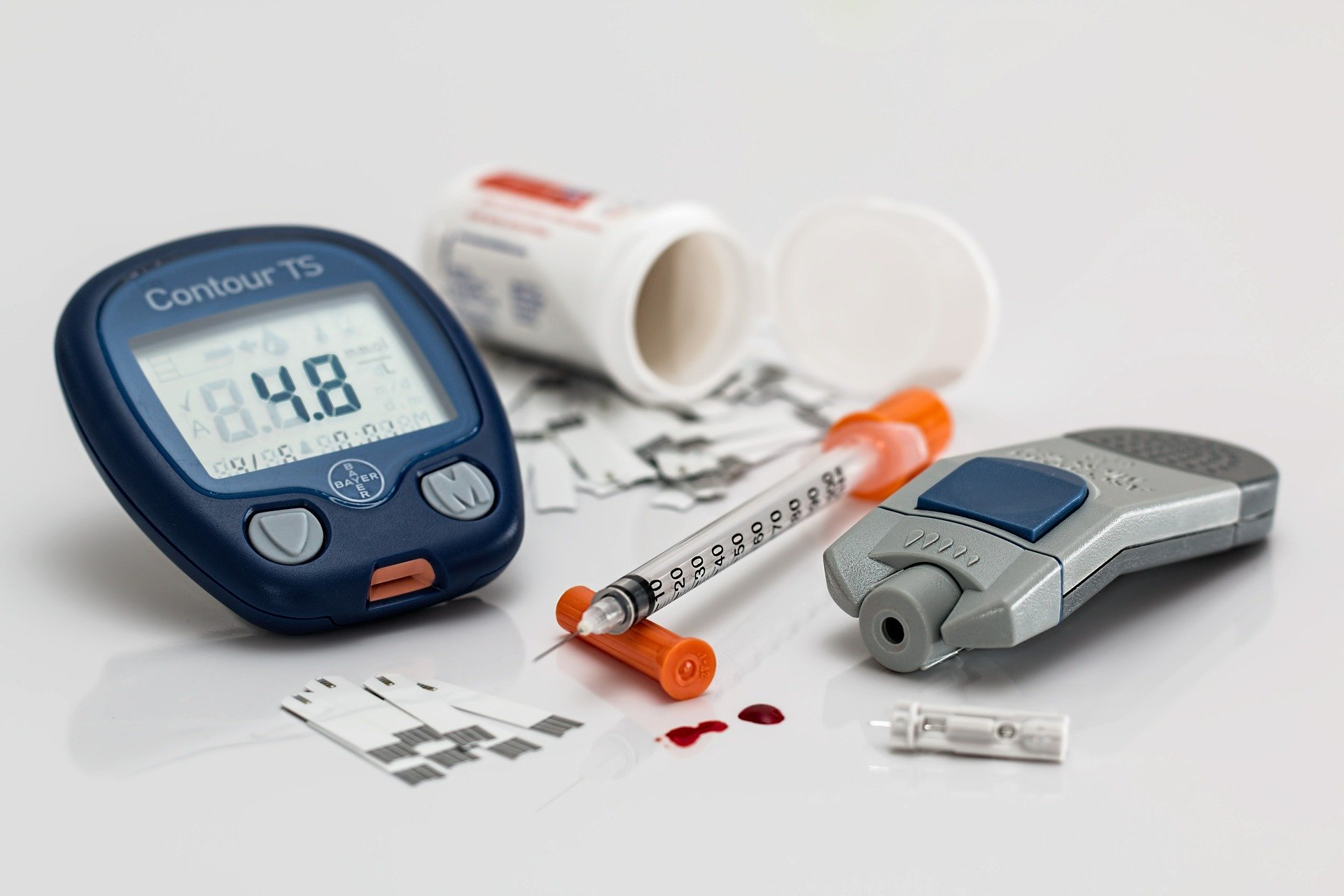
Type 1 Diabetes and New Technologies
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease of genetic and environmental causes that usually arises during childhood or adolescence. Its progression is rapid and leads to the almost complete loss of the pancreatic islets that make and release into the blood the hormone insulin as well as others related to blood sugar control. Therefore, an early detection of the disease and an immediate therapeutic approach is required in order to delay disease
PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR

Dra. María Soledad Ruiz de Adana
UGC Endocrinología y Nutrición
Hospital Regional de Málaga – IBIMA
Servicio de Endocrinología y Nutrición
Pabellón 1, sótano, Hospital Civil
Plaza del Hospital Civil s/n,
29009, Malaga (Spain)
Teléfono/Fax: +34 951 290 343 / +34 951 290 302
Contact
Ongoing and finished grants in the last five years
Modulation of the endocannabinoid system in islets of Langerhans as a therapy against the autoimmune destruction occurring in type 1 diabetes.
TEAM MEMBER
TIME: 2019-2021 BUDGET: 60,450€
FINANCIADO POR: Consejeria de Salud y Familias de Andalucía

Impact of insulin analogues on oxidative stress and inflammation in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR
TIME: 2018-2020 BUDGET: 99,220€
FINANCIADO POR: Instituto de Salud Carlos III

Randomized crossover clinical trial in patients with type 1 diabetes under treatment with continuous subcutaneous insulin infuser to evaluate the impact of telemedicine versus conventional clinical practice. Comprehensive Clinical Impact and Costs.
PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR
TIME: 2013-2015 BUDGET: 40,133€.
FINANCIADO POR: Consejería de Salud, Junta de Andalucía

New technologies por optimizing nutritional properties and production of goat milk and related products in Andalusia (CAPRITEC).
TEAM MEMBER
TIME: 2013-2014 BUDGET: 119,000€
FINANCIADO POR: CDTI-FEDER – INTERCONNECTA

Relevant Publications
Ruiz de Adana MS, Alhambra-Expósito MR, Muñoz-Garach A, Gonzalez-
Molero I,Colomo N, Torres-Barea I, Aguilar-Diosdado M, Carral F, Serrano M, Martínez-Brocca MA, Duran A, Palomares R; Diabetes Group of SAEDYN (Andalusian Society of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Nutrition). Randomized Study to Evaluate the Impact of Telemedicine Care in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes With Multiple Doses of Insulin and Suboptimal HbA in Andalusia (Spain): PLATEDIAN Study. Diabetes Care. 2020 Feb;43(2):337-342. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0739. Epub 2019 Dec 12. PMID: 31831473.
Molero I,Colomo N, Torres-Barea I, Aguilar-Diosdado M, Carral F, Serrano M, Martínez-Brocca MA, Duran A, Palomares R; Diabetes Group of SAEDYN (Andalusian Society of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Nutrition). Randomized Study to Evaluate the Impact of Telemedicine Care in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes With Multiple Doses of Insulin and Suboptimal HbA in Andalusia (Spain): PLATEDIAN Study. Diabetes Care. 2020 Feb;43(2):337-342. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0739. Epub 2019 Dec 12. PMID: 31831473.
Colomo N, López-Siguero JP, Leiva I, Fuentes N, Rubio-Martín E, Omiste A,Guerrero M, Tapia MJ, Martín-Tejedor B, Ruiz de Adana MS, Olveira G.
Relationship between glucose control, glycemic variability, and oxidative stress in children with type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2019 Nov;66(9):540- 549. English, Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2018.12.010. Epub 2019 Mar 8. PMID: 30853269.
Relationship between glucose control, glycemic variability, and oxidative stress in children with type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2019 Nov;66(9):540- 549. English, Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2018.12.010. Epub 2019 Mar 8. PMID: 30853269.
Roca-Rodríguez MDM, Ayala-Ortega MC, Jiménez-Millán AI, García Calzado
MC, Ruiz de Adana MS, Carral-San Laureano F. Unilateral renal agenesis and abrupt onset diabetes: an unfrequent form of MODY type diabetes. Med Clin (Barc). 2019 Jan 4;152(1):19-21. English, Spanish. doi 10.1016/j.medcli.2017.12.020. Epub 2018 Mar 7. PMID: 29525113.
MC, Ruiz de Adana MS, Carral-San Laureano F. Unilateral renal agenesis and abrupt onset diabetes: an unfrequent form of MODY type diabetes. Med Clin (Barc). 2019 Jan 4;152(1):19-21. English, Spanish. doi 10.1016/j.medcli.2017.12.020. Epub 2018 Mar 7. PMID: 29525113.
Giménez M, Díaz-Soto G, Andía V, Ruíz de Adana MS, García-Cuartero B,
Rigla M, Martínez-Brocca MA; en nombre del Grupo de Tecnologías Aplicadas a la Diabetes de la SED y de la SEEP. SED-SEEP Consensus document on the use of continuous glucose monitoring in Spain. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2018 Mar;65 Suppl 1:24-28. English, Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2017.03.011. Epub 2017 May 18. PMID: 29412165.
Rigla M, Martínez-Brocca MA; en nombre del Grupo de Tecnologías Aplicadas a la Diabetes de la SED y de la SEEP. SED-SEEP Consensus document on the use of continuous glucose monitoring in Spain. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2018 Mar;65 Suppl 1:24-28. English, Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2017.03.011. Epub 2017 May 18. PMID: 29412165.
Rubio-Martín E, García-Escobar E, Ruiz de Adana MS, Lima-Rubio F, Peláez L, Caracuel AM, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, Soriguer F, Rojo-Martínez G, Olveira G. Comparison of the Effects of Goat Dairy and Cow Dairy Based Breakfasts on Satiety, Appetite Hormones, and Metabolic Profile. Nutrients. 2017 Aug 15;9(8):877. doi: 10.3390/nu9080877. PMID: 28809789.
Ruiz-de-Adana MS, Dominguez-Lopez ME, Gonzalez-Molero I, Machado A, Martin V, Cardona I, de-la-Higuera M, Tapia MJ, Soriguer F, Anarte MT, Rojo-Martínez G. Comparison between a multiple daily insulin injection regimen (basal once-daily glargine plus mealtime lispro) and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (lispro) using continuous glucose monitoring in metabolically optimized type 1 diabetes patients: A randomized open-labelled parallel study. Med Clin (Barc). 2016 Mar 18;146(6):239-46. doi:10.1016/j.medcli.2015.09.020. Epub 2015 Dec 4. PMID: 26656958.
Ruiz de Adana MS, Colomo N, Maldonado-Araque C, Fontalba MI, Linares F, García-Torres F, Fernández R, Bautista C, Olveira G, de la Cruz JL, Rojo-
Martínez G, Valdés S. Randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of
insulin glargine vs. NPH insulin as basal insulin for the treatment of glucocorticoid induced hyperglycemia using continuous glucose monitoring in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and respiratory disease. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015 Nov;110(2):158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.09.015. Epub 2015 Sep 30. PMID: 26474657.
Martínez G, Valdés S. Randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of
insulin glargine vs. NPH insulin as basal insulin for the treatment of glucocorticoid induced hyperglycemia using continuous glucose monitoring in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and respiratory disease. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015 Nov;110(2):158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.09.015. Epub 2015 Sep 30. PMID: 26474657.
Lago-Sampedro AM, Gutiérrez-Repiso C, Valdés S, Maldonado C, Colomo N,
Almaraz MC, Rubio-Martín E, Morcillo S, Esteva I, Ruiz de Adana MS, Perez-Valero V, Soriguer F, Rojo-Martínez G, García-Fuentes E. Changes in thyroid function with age: results from the Pizarra population-based longitudinal study. Int J Clin Pract. 2015 May;69(5):577-87. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12545. Epub 2015 Jan 21. PMID: 25604441.
Almaraz MC, Rubio-Martín E, Morcillo S, Esteva I, Ruiz de Adana MS, Perez-Valero V, Soriguer F, Rojo-Martínez G, García-Fuentes E. Changes in thyroid function with age: results from the Pizarra population-based longitudinal study. Int J Clin Pract. 2015 May;69(5):577-87. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12545. Epub 2015 Jan 21. PMID: 25604441.
Martínez-Brocca MA, Morales C, Rodríguez-Ortega P, González-Aguilera B, Montes C, Colomo N, Piédrola G, Méndez-Muros M, Serrano I, Ruiz de Adana MS, Moreno A, Fernández I, Aguilar M, Acosta D, Palomares R. Implementation of subcutaneous insulin protocol for non-critically ill hospitalized patients in andalusian tertiary care hospitals. Endocrinol Nutr. 2015 Feb;62(2):64-71. English, Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Nov 20. PMID: 25467634.
Esmatjes E, Jansà M, Roca D, Pérez-Ferre N, del Valle L, Martínez-Hervás S, Ruiz de Adana M, Linares F, Batanero R, Vázquez F, Gomis R, de Solà-Morales O; Telemed-Diabetes Group. The efficiency of telemedicine to optimize metabolic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Telemed study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014 Jul;16(7):435-41. doi: 10.1089/dia.2013.0313. Epub 2014 Feb 14. PMID: 24528195.